Alcohol-Based Hand Cleaners Can Cause Rashes
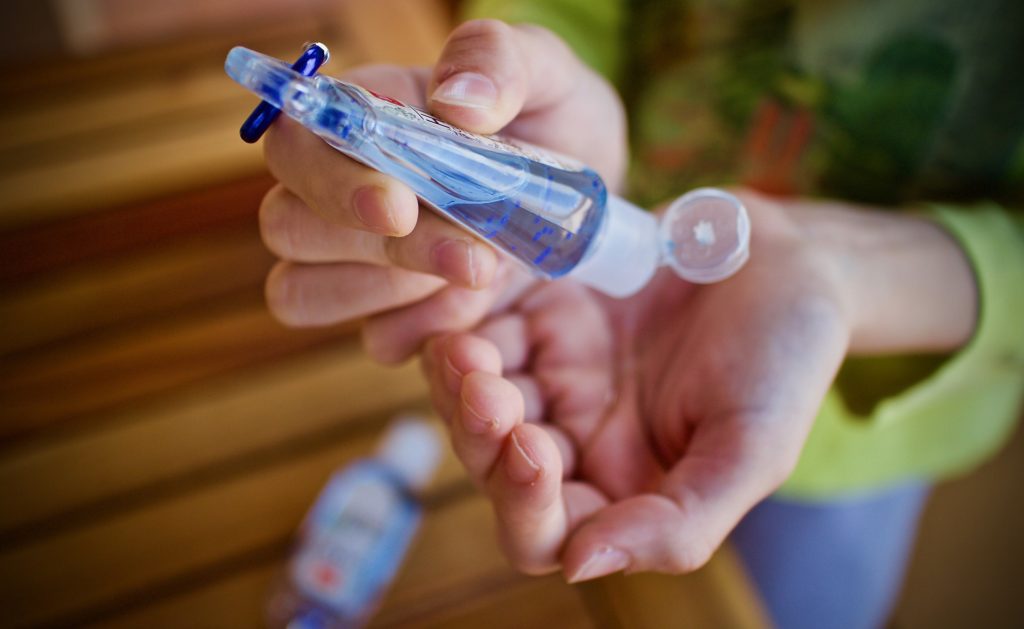
The use of alcohol-based hand sanitizers (ABHS) can cause skin reactions and allergies for some people which can manifest in dryness, itchiness, erythema (a redness, infection, or inflammation of the skin), and bleeding in severe situations. Repeated use of ABHS can cause the drying of skin on the hands, which can lead to peeling or cracking. Among the ABHS varieties, the most irritating to the skin are n-propanol and isopropanol.
Research indicates HOCl kills germs on the hands quicker than isopropyl alcohol-based hand sanitizers, and it does not cause any skin problems. Unlike ABHS products, HOCl heals the skin while it kills germs on the hands: a real win-win. To read more on how HOCl compares against alcohol as a hand-based sanitizer, click here and here.
HOCl Inside has compiled research that you might also find useful. For example, if you wish to discover why HOCl is effective as a microbicidal agent, then click here. For an explanation on how HOCl was discovered to be an effective disinfectant, click here. For more detail on the various factors affecting HOCl efficacy, click here.
